So, you’ve read and re-read the academic writing assignment that you received from your professor, and now you’re staring at a blank page.
Does your mind feel as blank as the page? Are you Frozen by fear? Rubbing your eyes with exhaustion?
Whether you’re writing an essay for a community college in Boston, Massachusetts or a university in New England, USA, you need to start somewhere. Brainstorming means you use your imagination and prior knowledge to collect thoughts. After gathering a great quantity of ideas, you select the highest quality ideas.
Filling that empty white document can feel like leaping into unknown icy water. Brainstorming is the way to warm up for a deep dive into the EAP topic.
Brainstorming begins with simple questions. What do you know about the topic? What do you want to learn about the topic?
As you brainstorm, you journey farther down the academic writing quest. How do you narrow down a topic into a thesis? How do you gather the examples and evidence necessary for an academic essay?
Here are EAP brainstorming strategies to jumpstart the engine of your creativity.
Brainstorming tip #1: Freewriting
Do you have no ideas? Or the opposite problem—too many ideas?
Freewriting means what it sounds like—you’re free to write whatever comes to mind. The point is not to make it perfect—not even necessarily to make it good—but just to put thoughts on paper—no rules, no revising. You can even write about how you don’t know what to write about.
The only limit you should set for yourself is that you write for a specific period of time—let’s say 30 minutes—or for a specific number of pages—let’s say 2 pages. Non-stop activity gets the juices flowing, and a concrete goal gives you satisfaction. Here’s an example of freewriting:
This essay is supposed to be about the Boston Tea Party but I don’t know anything about US history except that the American Revolution happened a long time ago (when???) somewhere in Massachusetts or maybe I’m wrong. I can’t think of anything else to say and now the clock says two minutes, I’ll keep babbling anyway. Boston, MA, politics, tea. My grandmother used to make tea when I stopped by after my English courses. But that’s not useful for this essay. Or maybe there’s a connection. Hmmm… I remember the professor talked about the taxes in the New English states (colonies?) and my grandmother used to complain about paying high taxes at the market and…
Freewriting stimulates your brain the same way physical exercise wakes up your mind.
Brainstorming tip #2: Making a Cube
Draw a cube in your notebook. Each of the six sides has a task:
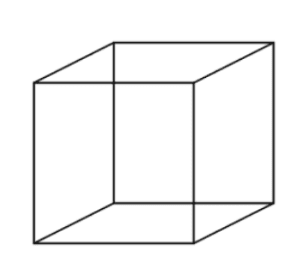
Side 1: Describe the topic.
Side 2: Compare the topic.
Side 3: Connect the topic.
Side 4: Classify the topic.
Side 5: Argue for or against the topic.
Side 6: Personalize the topic.
Instead of those 6 tasks, you could replace those verbs with other academic tasks: apply, analyze, question, connect, define, classify, associate, or explain cause and effect—whichever inspire ideas.
Imagine your topic is attending university in the U.S. Next to each point on the cube, you would write words and phrases inspired by the verb at hand:
Side 1: Describe: Exciting, difficult, expensive, growing opportunities, expensive, valuable.
Side 2: Compare: Different from my country. USA = more essay writing, dorms with roommates, critical thinking, fewer standardized exams and lectures, smaller classes.
Side 3: Connect: student visa policies, US immigration law, IELTS, TOEFL iBT, travel restrictions from covid-19, globalization means more English at work.
Side 4: Classify: community colleges (Holyoke, Greenfield), state universities (UMASS Boston), private ivy league (Harvard) graduate schools, MBA, BA, MFA programs.
Side 5: Argue for: opens doors, better jobs, international workplace, investment in future, social networking, broadens horizons.
Side 6: Personalize: my cousin > engineering degree, MIT internship, campus resources help with culture shock (which worries me.) IELTS stresses me out!!!! Way to avoid?
This brainy approach works if you like approaching topics from different angles.
Brainstorming tip #3: Clustering
When you cluster, you draw bubbles and connect words and concepts associated with the topic—anything that comes to mind.
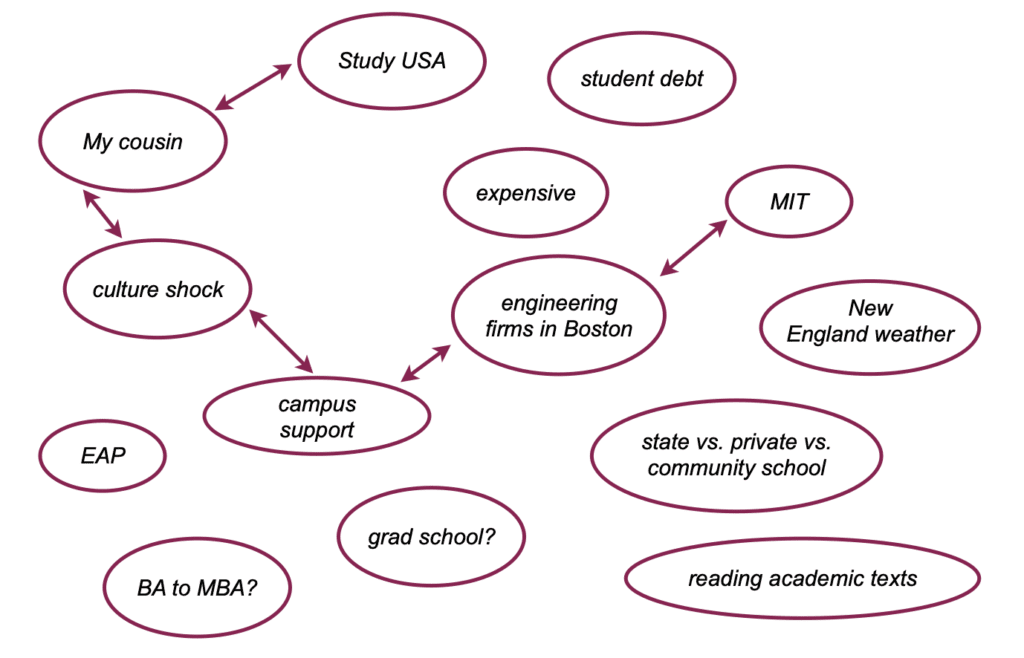
This visual method works when you have a lot of random thoughts and you are trying to “see” connections.
Brainstorming tip #4: Bulleting
With this technique, you make bulleted lists with concepts, terms, and ideas. This can help you narrow down from the first list to a second list. The list on the left contains general bullet points, while the list on the right expands on a single bullet to delve deeper.
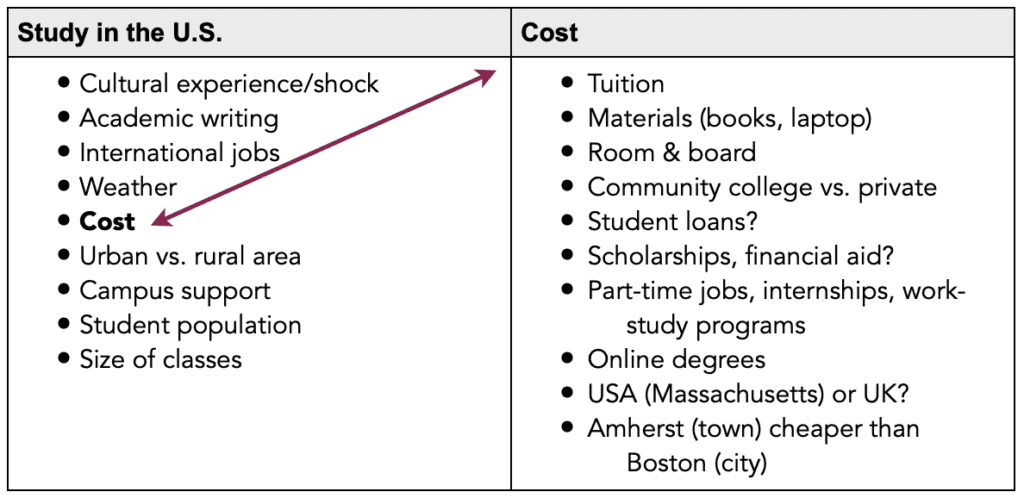
This method works great if you’re an orderly person who likes making lists.
Brainstorming tip #5: Venn Diagram
The famous Venn diagram technique works well for brainstorming differences and similarities between two topics. You draw two intersecting circles and write the qualities they share in the middle where the circles intersect and the qualities that are unique in the left and right spaces. For example, let’s say you’re brainstorming differences and similarities between two cities in Massachusetts, Boston and Northampton.
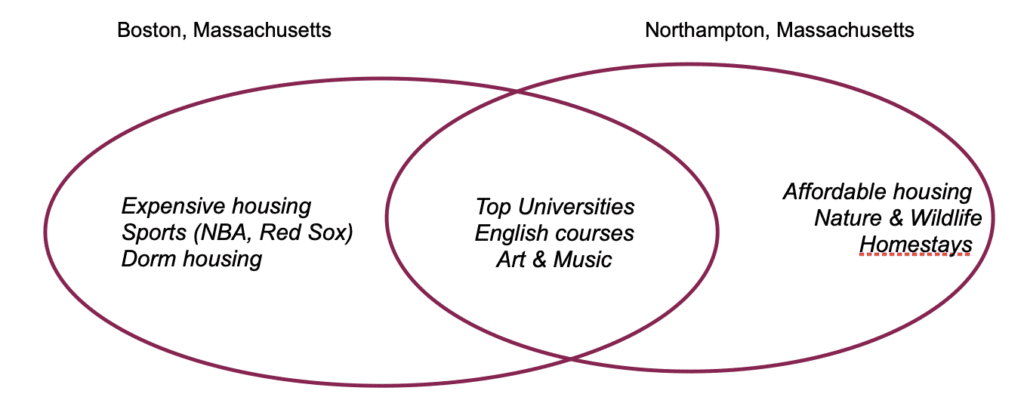
This famous brainstorming method is used in the academic and business worlds because it so clearly shows differences and similarities.
To analyze relationships among three topics, you can make a Venn diagram with three circles. The 3-circle helps visualize and understand complex connections. You brainstorm three basic questions. Which qualities are unique to each? Which traits do any two topics have in common? Which similarities are shared by all three topics?
Brainstorming tip #6: Tree diagram
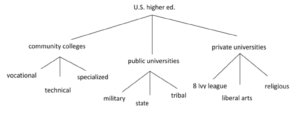
The tree diagram begins with a central idea that branches off into categories or supporting ideas.
Imagine you’re brainstorming different types of schools in US higher education.
Tree diagrams are perfect for brainstorming classification essays. You could also draw tree diagrams to brainstorm effects, starting with a cause at the top and branching off into increasingly specific downstream effects. Pretty cool, huh?
Brainstorming tip #7: Journalist Dice
Dice aren’t just toys for games and gambling–they can be a tool for writing. Rolling journalist dice is a stimulating way to flesh out narrative essays. Each side of the die corresponds to one of the 6 question words. To make the game fun, roll a die, and write down one answer the question every time you roll. Roll at least a dozen times to write down a variety of details and ideas.

In addition to building a narrative essay, this brainstorming technique can help you develop a compelling story for your college application essay. For the tired and uninspired writer, the game element of rolling dice makes the writing process more engaging and enjoyable.
Brainstorming tip #8: T diagram
Besides the Venn diagram, another two-sided brainstorming technique for compare/contrast, pro/con, and advantage/disadvantage essays is the T diagram.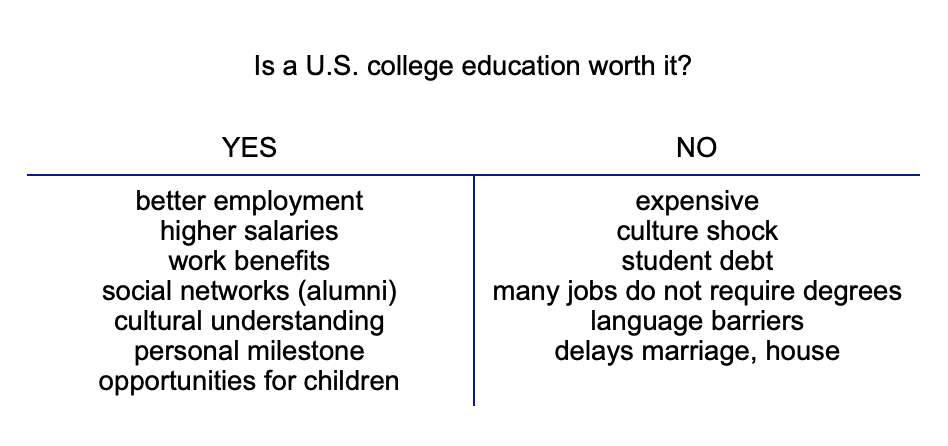
This method works well if you like thinking in terms of opposites. Can you say “On the one hand” and “On the other hand”?
What’s next in the writing process?
After your fast and furious brainstorm, the next step is to create an outline. When you outline, you pick your best and brightest ideas. Then you begin organizing them into a coherent, linear argument. You select and sort supporting points, evidence, examples, and elaboration. To learn more about outlining, click here for the next article in our academic writing series.
The best way to improve your writing is to join an academic or business English course. With guidance from an expert instructor and feedback from a community of peers, you can master the art of academic writing.
Related Articles
- How to improve your academic and business English writing skills
- Why 2021 has skyrocketed the importance of improving your English communication skills for the workplace?
- What is the difference between social and academic English, Part 1
- What is the difference between social and academic English, Part 2
- Top movies to help you learn English and love the language more
- Academic Writing Tip: Making an Outline